There are a many different derivatives of ImageJ with very similar names, and some confusion is inevitable. Below is a table which should help to clarify the purpose of each. For the historical context of these projects, see History below.
| Name | Author/Maintainer(s) | Description | Initiated | Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ImageJ | Wayne Rasband | The original version of ImageJ which has been in development since 1997. It has a strong, established user base, with thousands of plugins and macros for performing a wide variety of tasks. Sometimes referred to as the original ImageJ or ImageJ 1.x for technical clarity, or informally with the shorthands ImageJ1 or IJ1. | 1997 | Active | |
| ImageJ2 | ImageJ2 developers | A new version of ImageJ targeting scientific multidimensional image data. It is a complete rewrite of the original ImageJ, but includes the original ImageJ with a compatibility layer, so that old-style plugins and macros can run the same as always. ImageJ2 provides several significant new features, such as an automatic updater, and improved scripting capabilities. | Dec. 2009 | Active | |
| Fiji | Fiji contributors | Fiji is Just ImageJ, with extras. It is a distribution of ImageJ and ImageJ2 with many plugins useful for scientific image analysis in fields such as life sciences. It is actively maintained, with updates released often. | Dec. 2007 | Active | |
| ImageJ.JS | Wei Ouyang | ImageJ.JS is a web version of ImageJ that runs in the browser without installation, compiled from Java to JavaScript using the Cheerpj compiler and integrated with the ImJoy plugin system. It's accessible from https://ij.imjoy.io and also supports mobile devices and tablets. | 2020 | Active | |
| ImageJFX | Cyril Mongis | ImageJFX is a new user interface for ImageJ, built using JavaFX. | 2015 | Abandoned | |
| ImageSXM | Steve Barrett | Image SXM is a version of NIH Image that has been extended to handle the loading, display and analysis of scanning microscope images. | May 1993 | Active | |
 |
AstroImageJ | John Kielkopf | AstroImageJ is ImageJ with astronomy plugins and macros installed. | Unknown | Active |
| ImageJ2x | Rawak Software | ImageJ2x is a fork of the original ImageJ, modified to use a Swing interface. | Unknown | Last update: May 2015 |
|
| Closed-source variants | |||||
 |
SalsaJ | EU-HOU | SalsaJ is a closed-source fork of the original ImageJ intended for use with professional astronomy images. It was designed to be used in classrooms, and has been localized into over 30 different languages. | Unknown | Last update: Oct. 2012 |
| Obsolete variants | |||||
| MBF ImageJ | Tony Collins | The MBF "ImageJ for Microscopy" bundle (formerly
WCIF
ImageJ) is a collection of plugins and macros, collated and
organized by the MacBiophotonics facility. It went hand in hand with a comprehensive manual describing how to use the bundle with light microscopy image data. It was a great resource by microscopists, for microscopists. Unfortunately, the manual went offline in late 2012. In response, the software team at LOCI created the Cookbook user guide and update site, which includes most of the same plugins. |
2005 | Defunct (Last update: Dec. 2009) |
|
| ImageJA | Wayne Rasband (author); ImageJ2 team (maintainers) | ImageJA was a project that provided a clean Git
history of the original ImageJ, with a proper pom.xml file
so that it could be used with Maven without hassles. The ImageJ project
has since been updated to deploy releases to Maven Central directly,
without the need for the ImageJA project as an intermediate. |
Jul. 2005 | Superseded by ImageJ | |
| ImageJX | Grant Harris | ImageJX was created as a means to discuss and explore improvements to ImageJ. There was an ImageJX mailing list as well as an ImageJX software prototype. The ImageJX software prototype was a proof of concept—an attempt to reorganize ImageJ's internals to make it more flexible. The prototype demonstrated this flexibility by recasting the program in Swing. The ImageJX project formed the basis of an application to NIH for funding, which is what launched the ImageJ2 project (see above). | Mar. 2009 | Superseded by ImageJ2 | |
| NIH Image | Wayne Rasband | NIH Image is a public domain image processing and analysis program for the Macintosh. It is the direct predecessor of ImageJ, and is no longer under active development (though see ImageSXM above). | 1993 or earlier | Superseded by ImageJ | |
History
The first imaging program that Wayne Rasband developed, starting in the late 70s, was called simply “Image”. It was written in Pascal, ran on PDP-11 minicomputers and ran in only 64KB of memory! Rasband started work on the second, NIH Image, in 1987 when the Mac II became available. Rasband was a Mac enthusiast, and the Mac II had card slots just like the PDP-11. Rasband started work on ImageJ in 1997, when Java was becoming popular. Rasband was intrigued by the idea of creating a version of NIH Image that would “run anywhere”, including as an applet in Web browsers.
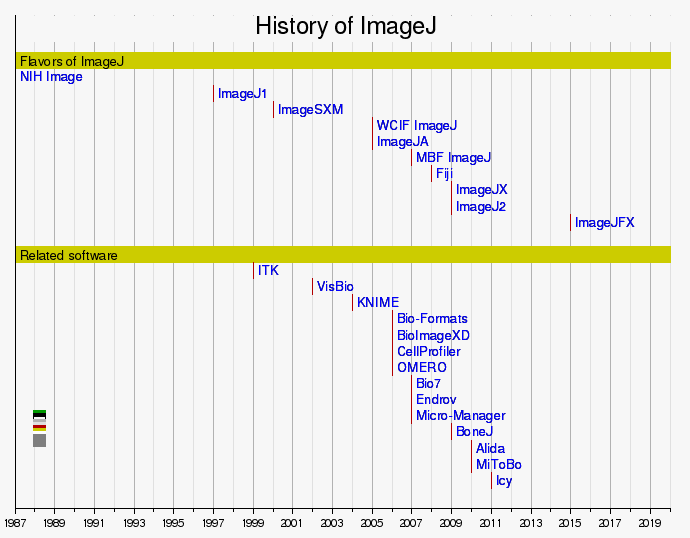
Timeline
Here is a timeline of software development related to ImageJ:
Publications
See also Citing.