A new minor version of TrackMate_ has been released. This page lists the changes that are visible to the user.
Version 2.1.0 focuses mainly on performance and usability improvements for manual editing and manual tracking using TrackMate. It also features GUI improvements.
We are grateful to Jan Brocher and Masanari Takamiya for comments and bug reports during the release candidate process.
Highlights
- Major rewrite of the core track model to achieve a far better performance when manually editing a very large datasets. You can now interactively edit large datasets without the GUI becoming too sluggish.
- You can now preview the detection parameters on the current frame before applying it to the whole data:
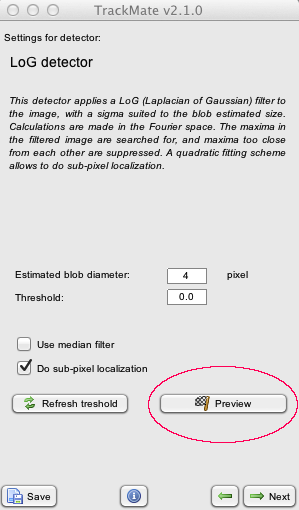
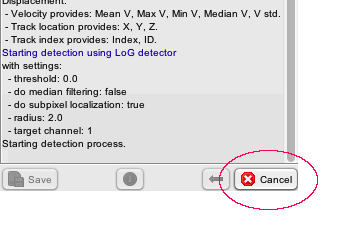
- The detection step is now interruptible in the GUI. A click on the cancel button will gracefully interrupt the detection process, and yields the spots found so far. They can be used later on normally.
- The HyperStack viewer and editor has now a configuration panel that has a log window and some tools for manual annotation:
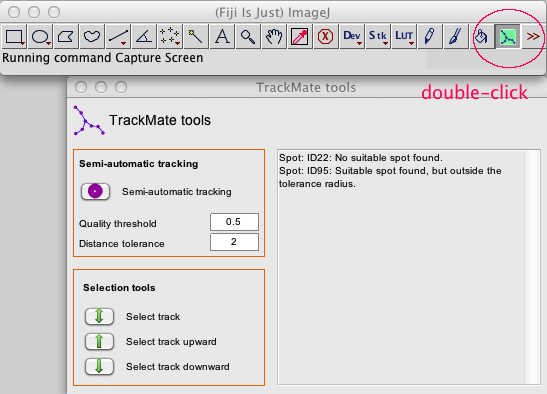
- Semi-automatic tracking: Select one (or more) spot, TrackMate will find its most likely successors:
- Re-design of TrackScheme. TrackScheme is now about 40 times faster to launch, even on large dataset. By default it uses the ‘simple’ style, and the update of the small thumbnails can be switched on/off.
- The ‘Load’ button was removed from the GUI. TrackMate files can be loaded from the Plugins › Tracking › Load a TrackMate file menu item.
- There is a new Plugins › Tracking › Manual tracking with TrackMate menu item, that launched another GUI stripped down for manual editing.
Backward incompatible changes
- The XML file format has changed, to include more data, and for better separability and reuse in other softwares. However, backward compatible loaders are present to ensure the loading and on-the-fly conversion with files generated by TrackMate versions above 1.2.
Improvements
- Better coloring scheme. There is a unique coloring scheme shared in all views.
- The GUI is now resizable.
Bug fixes
- A ‘Locale’ problem prevented the entering of numerical features correctly on system relying on other decimal separators that the dot. TrackMate now enforces the dot to be used as a decimal separator on all Locales. However there are still reports that this fails on Windows machine with exotic (i.e. non dot as decimal separator) locales.
- Numerous other bugfixes.
Jean-Yves Tinevez 05:03, 5 August 2013 (CDT)