Scijava-parallel is a framework that provides an access point for using computational resources such as remote computers or HPC clusters. It hides details about configuration and initialization of such resources.
Types of users
Scijava-parallel is designed to be used by three types of users and we call them: developers, Fiji users and parallelization paradigm providers.
A Developer is a user who uses its defined API for accessing configured computational resources. Remote computational resources are accessible through components that implement an interface derived from the interface ParallelParadigm. These components are called parallelization paradigm implementations and specialized interfaces are called parallelization paradigms.
A Fiji user provides configurations for parallelization paradigm implementations. The configurations are called profiles. Users also select one configuration that is used when some code requests a parallelization paradigm.
A parallelization paradigm provider offers new parallelization paradigm implementations or new types of parallelization paradigm.
Developers
Developers obtain parallelization paradigm implementation that is in selected profile by method getParadigmOfType. Desired parallelization paradigm is specified when the method is called. If the parallelization paradigm implementation does not exist, null value type is returned.
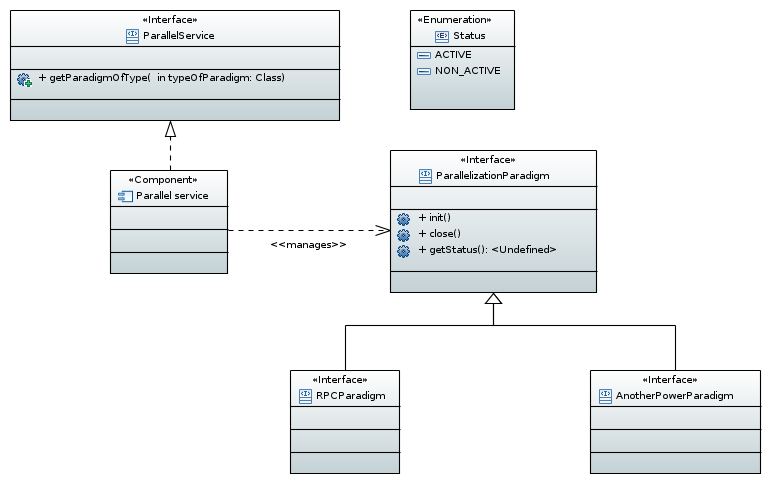
Figure 1: ParallelService UML class diagram.
Base type ParallelParadimg contains three methods:
init- initializes resources required for run and used by parallelization paradigm;close- disposes initialized resources;getStatus- returns status indicating whether the paradigm is initialized or disposed.
The first parallelization paradigm of type RPCParadigm has methods:
List<Map<String, Object>> runAll(String commandName, List<Map<String, Object>> parameters)
List<CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>>> runAllAsync(String commandName, List<Map<String, Object>> parameters);
The methods cause parallel execution of specified command for parameters. A size of a parameters define how many executions are to be performed. Parallelization and distribution of requests is solved internally by parallelization paradigm implementation. There are three implementations of parallelization paradigms:
LocalMultithreadedParadigm
LocalMultithreadedParadigm in the module scijava-parallel executes commands in the same instance of running Fiji and uses multiple threads for parallelization.
FSTRPCParadigm
FSTRPCParadigm in the module scijava-parallel-fst executes commands in different instances of running Fiji. Fiji can run in a different computer or an HPC cluster. Communication is realized through TCP/IP connection and data are serialized by fst library fst.
It is implementation of RPCParadigm that executes commands in different instances of running Fiji. The Fiji can run in a different computer or a HPC cluster. Communication is realized through TCP/IP and data are serialized by library fst. It is possible to send as parameter in request every serializable object . Support for another types could be added through the offered extensibility. It is necessary to implement the interface ParallelizationParadigmSerializer:
public interface ParallelizationParadigmSerializer extends SciJavaPlugin {
void writeObject(Object obj, ObjectOutput output) throws IOException;
Object readObject(Class<?> objectClass, ObjectInput input) throws IOException;
Class<?> getSerializedClass();
boolean alsoForAllSubclasses();
boolean willHandleClass(Class<?> clazz);
}
and to annotate the implementing class with @Plugin annotation with specified type ParallelizationParadigmSerializer. There exists one implementation of the interface for the type Dataset in the project scijava-parallel-fst:
@Plugin(type = ParallelizationParadigmSerializer.class)
public class DatasetSerializer implements ParallelizationParadigmSerializer {
ImageJServerParadigm
ImageJServerParadigm in the module scijava-parallel-imagej-server also executes commands in different instances of running Fiji. The paradigm uses ability of imagej-server to execute commands through its provided REST API.
Fiji users
Scijava-parallel offers plugin that provides management of paradigms and profiles. It is accessible from menu Plugins › Scijava parallel › Paradigm Profiles Manager. The plugin shows the following form:
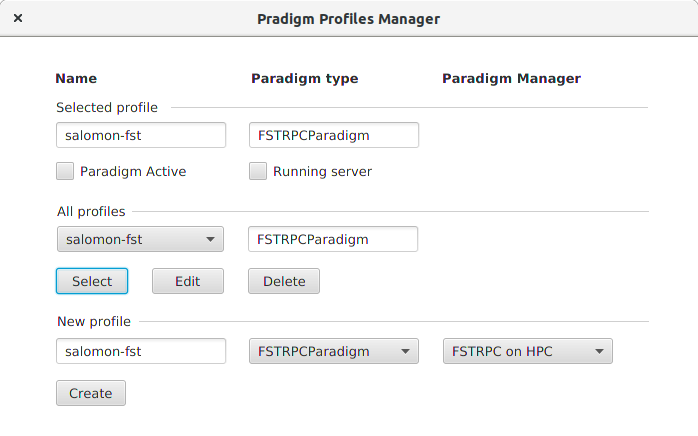
Figure 2: Paradigm Profiles Manager
Profiles can be:
- created - button at the bottom;
- edited - button in the central part;
- deleted - button in the central part; and
- selected - button in the central part.
Profile creation and editing
During the creation of a profile a user specifies the implementation of an associated paradigm - FSTRPCParadigm is selected in the screenshot - paradigm manager. Paradigm managers are supplied by parallelization paradigm providers together with parallelization paradigm implementations. Paradigm managers manage resources used by a parallelization paradigm implementation. There are three paradigm managers available that differ in the location where they start a server handling requests:
- Inprocess FSTPRC - in an actual running instance of Fiji;
- Local FSTRPC - on a local machine as an another process;
- FSTRPC on HPC - on a remote HPC cluster through ssh.
This is done in order to allow the user to provide basic settings during a profile creation. The settings required changes according to the selected paradigm manager. Local FSTPRC paradigm manager requires the user to provide the path to a Fiji installation in a local filesystem while FSTRPC on HPC requires the user to provide information that will allow connection to a remote HPC cluster - host name, credentials - and the location of a Fiji installation on HPC cluster.
Profile selection
This action marks a paradigm profile as selected. An instance of the paradigm associated with a selected profile is returned as the result of calling the method getParadigmOfType in case that the parallelization paradigm implementation provides (implements an interface) a requested parallelization paradigm type. In the present implementation of the parallel service, only one profile can be marked as selected but we see it as an implementation detail that could be changed in the future.
Parallelization paradigm management
The manager enables the user to perform basic management of the parallelization paradigm implementation in the selected profile. The user can initialize and close the profile by the check box Paradigm Active. The paradigm manager FSTRPC on HPC offers a possibility to leave a Fiji, that is started in a job on a remote HPC, running while is an associated parallelization paradigm implementation closed. This property is specified by the user during
Parallelization paradigm providers
A Parallelization paradigm implementation requires only to implement one or more parallelization paradigms and to annotate this class as plugin:
@Plugin(type = ParallelizationParadigm.class)
public class MPIParadigmImpl implements MPIParadigm
The parallelization paradigm implementation very often also requires some specific initialization. The settings for the initialization are expected in an instance of ParallelizationParadigmProfile or its subclass. Scijava-parallel offers a framework for profile creation, its storing in persistent storage and paradigm initialization with contained settings. The framework provides the user interface described earlier.
The framework provides interface ParadigmManager and its implementation is used by the framework for a profile creation (method createProfile) and its editing (method editProfile). Parallelization paradigm implementation is initialized by the methodprepareParadigm. The parallelization paradigm provider implements the interface ParadigmManager and annotates it as @Plugin with a type ParadigmManager.
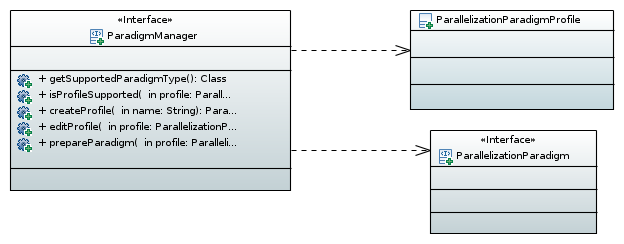
Figure 3: ProfilesManager UML class diagram.
The class ParadigmManagerUsingRunner supports the frequently occurring scenario of how ParallelizationParadigm is initialized: external software is launched - it is always Fiji in the case of the existing implementation - and parallelization paradigm is initialized with information on how to access the software (host name, port number). It works with profile type ParadigmProfileUsingRunner that contains an object of a type RunnerSettings or its subtype (e.g. LocalImagejRunnerSettings). ParadigmManagerUsingRunner starts external software through an interface ServerRunner. ParadigmManagerUsingRunner edits settings with an object that implements RunnerSettingsEditor. Implementing class should be annotated with the annotation @Plugin with the type RunnerSettingsEditor. It enables scijava-parallel to find an editor for a given type of settings. There are registered editors for existing implementations of RunnerSettings.
A developer makes a non-abstract child of the class ParadigmManagerUsingRunner. The child needs to implement only two abstract methods: getTypeOfRunner and initParadigm. It is possible to create a new implementation of ServerRunner or reuse one of the existing ones: LocalImagejRunner, HPCImageJRunner.
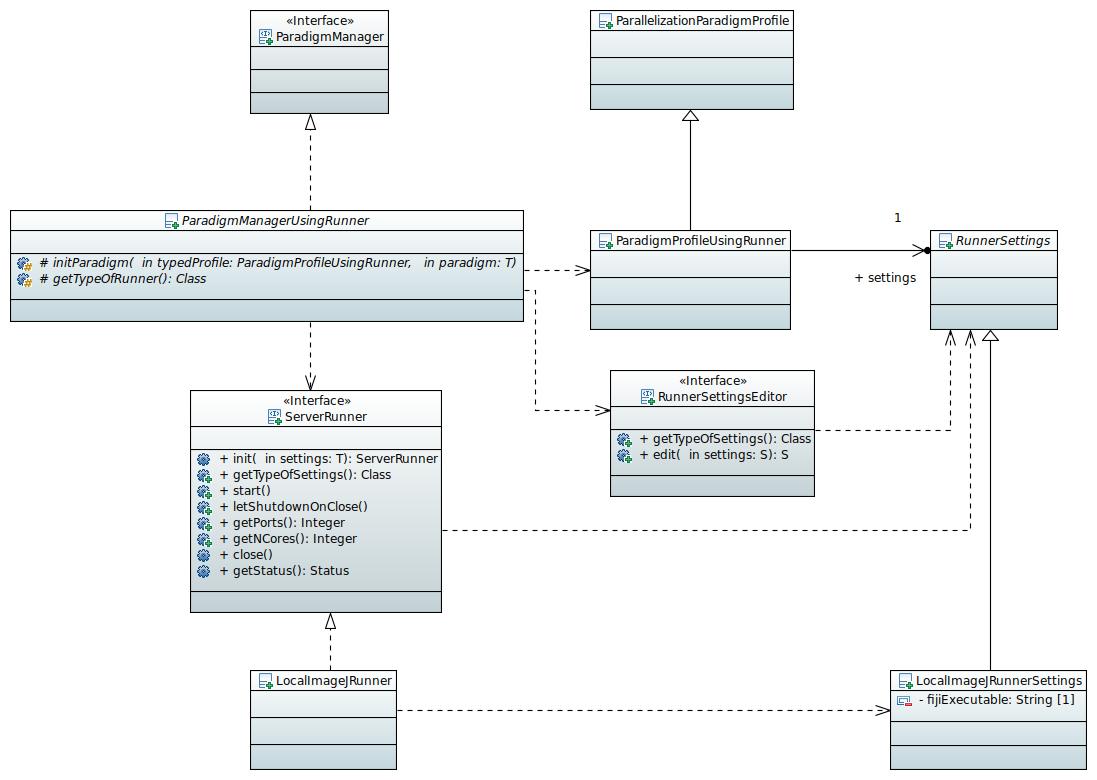
Figure 4: ParadigmManagerUsingRunner UML class diagram.
Installation
Scijava-parallel can be installed directly into Fiji from its update site https://sites.imagej.net/Scijava-parallel/. We also provide a modified version of Labkit that has support for scijava-parallel. This version of Labkit has its own update site https://sites.imagej.net/Imglib2-labkit-cluster/. It only demonstrates scijava-parallel and it is not meant as production software.