What is a sub scan?
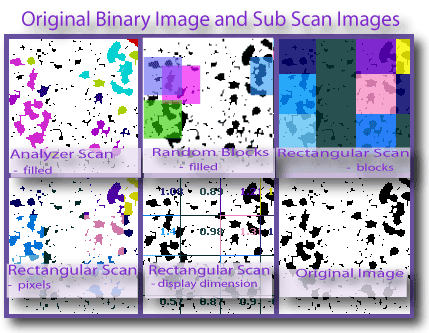
This page tells how to do and interpret a sub scan, which is a regular box counting scan applied to potentially many individual local areas of an image. The pictures below, which include graphics files generated as part of a sub scan, show the general idea of sub scanning.
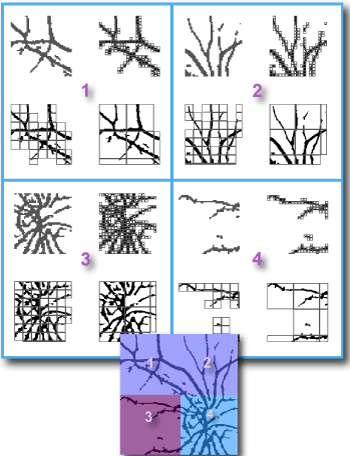
If you need to know the basics behind setting up a scan in general, go to the basic tutorial. For information on how to set up colour coding for the scanning described on this page, go here. For LCFD or local connected fractal dimension scans, click here.Sub scans show how locally calculated fractal dimensions are distributed in an image and how they depend on sample size. The images above illustrate the basic outputs of the two major types of subscan - particle analyzer and rectangular. The binary contours were automatically found by running a FracLac scan that invokes the ImageJ particle analyzer on one image as shown, then analyzes the detected particles as separate bodies.
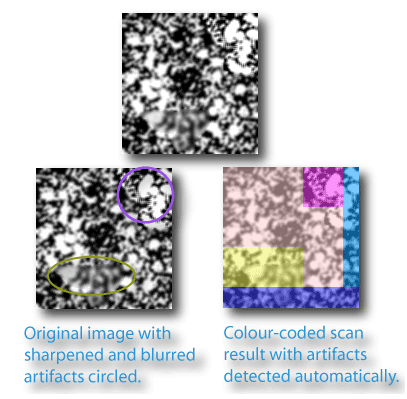
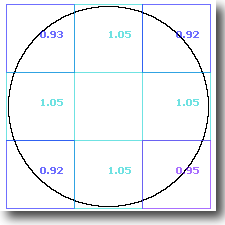
The others were rectangular scans. The grayscale texture was systematically scanned in blocks. That scan automatically detected two areas of difference in the texture, which are artifacts created using blurring and sharpening in ImageJ on ROIs on the original image. The artifacts are circled on the lower image. The results of the scan, the colour coded blocks, show the corresponding general areas where the differences were found as a difference in the local DBGray. The simple binary circle was scanned with a rectangular scan, to illustrate local variation attributable to digitization.
Results Files
In addition to graphics files like those you saw above,
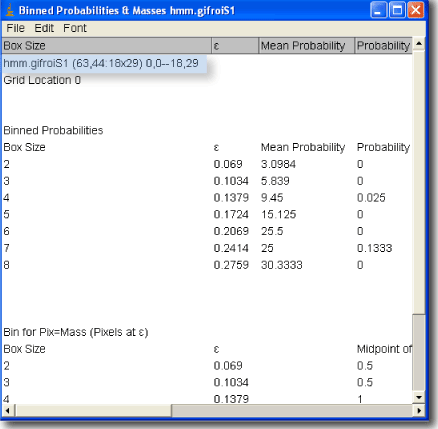
a sub scan generates results files. The main results file of a sub area scan is the same file as from a regular scan, except that it contains several rows for each image, corresponding to several samples taken during the sub area scan.
To interpret the results file from a subscan, see the main Results file page.
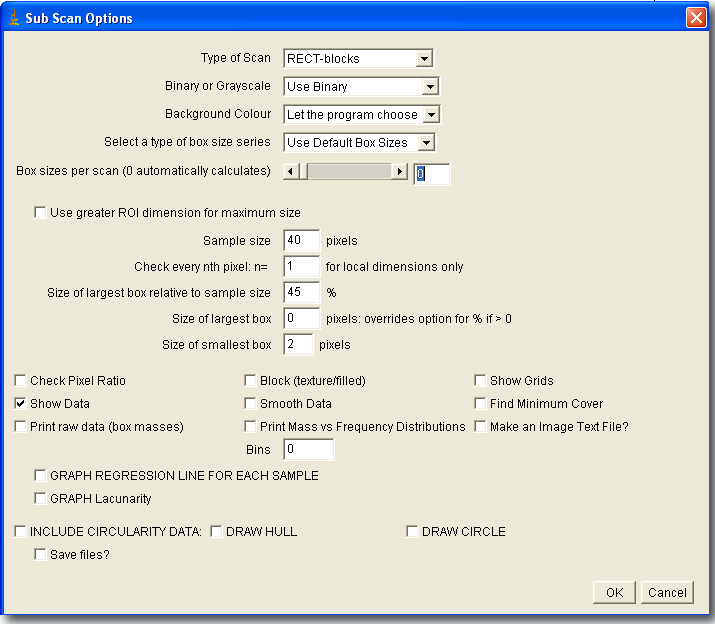
The screen shot below shows the options panel for a sub scan. Click on a part of the image or scroll past the image to the listings to find out what the settings are for and how to interpret their results.

 .
.