RETINA Analysis Toolkit
| RETINA Analysis Toolkit (ImageJ) | |
|---|---|
| Author | Daniel E. Maidana Demetrios G. Vavvas |
| Maintainer | Daniel E. Maidana Angiogenesis Laboratory Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School Email: Daniel Maidana |
| File | TUNEL Cell Counter Macro |
| Source | TUNEL Cell Counter Repository |
| Initial release | August 18th, 2015 |
| Latest version | July 21th, 2016 |
| Development status | Active and validated with Fiji (ImageJ 1.51d) |
| Website | RETINA Analysis Toolkit at YouTube |
RETINA Analysis Toolkit is a free macro toolkit designed and developed for Fiji (ImageJ). The purpose of the RETINA Analysis Toolkit is to perform fast quantitation of digital RGB images from retina cryosections, acquired by fluorescent microscopes. The current components of these toolkit are: TUNEL Cell Counter and RETINA Cell Heatmap.
Contents
TUNEL Cell Counter
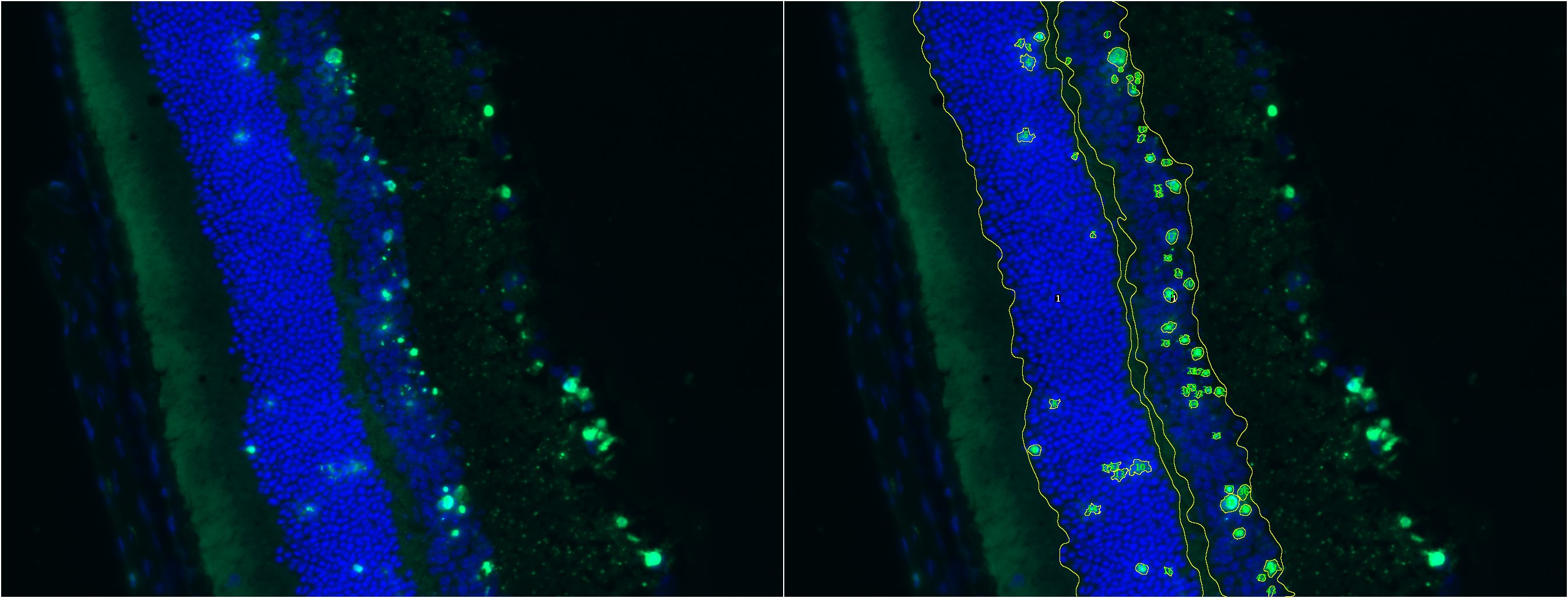
TUNEL Cell Counter is a customizable tool that processes digital images from retinal cryosections. It segments retinal outer nuclear (ONL) and inner nuclear layers (INL) and quantitates fluorescent-labelled cells in these layers.
Required Components
The following are required to execute this tool:
- TUNEL Cell Counter: Macro should be installed in Fiji (ImageJ).
- Digital Image: Files should be in TIFF format.
- Microscope Spatial Scale: Pixels/microns.
- Minimum Cell Size & Maximum Cell Area (µm2): These values should be determined upfront, according to your image dataset. These measurements can be performed in Fiji with the freehand selection tool, after setting the spatial scale factor.
How to Use: 2 Minute Tutorial
Processing Settings
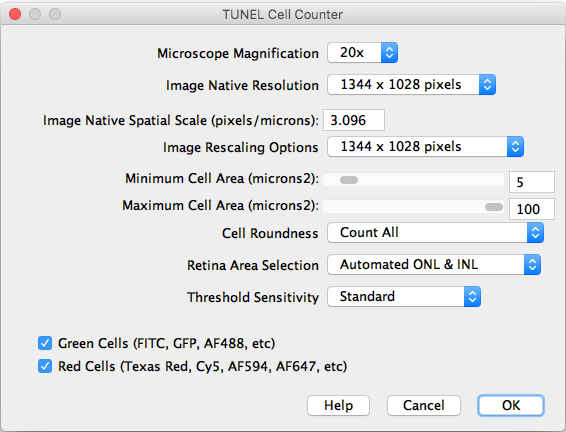
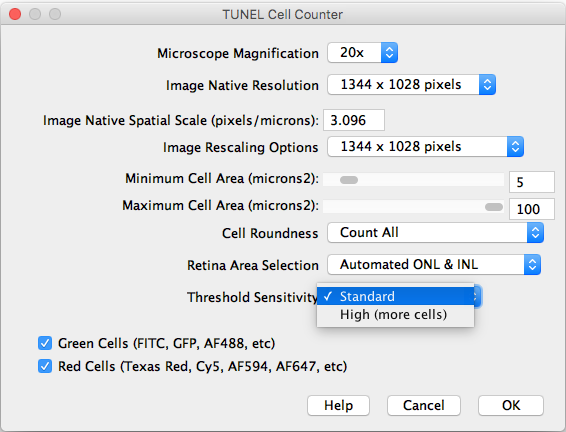
After importing a TIFF image and executing the counter, the following settings should be selected:
- Microscope Magnification: Displays the working 20x objective magnification.
- Image Native Resolution: Displays the imported image resolution.
- Native Spatial Scale: Input the current image scale in pixels/microns.
- Image Rescaling Options: If the image is larger that 1300 pixels width, it will be rescaled to speed up the processing. The rescaled image will be saved as a copy.
- Minimum and Maximum Cell Area: Input the previously measured and selected cutoff values.
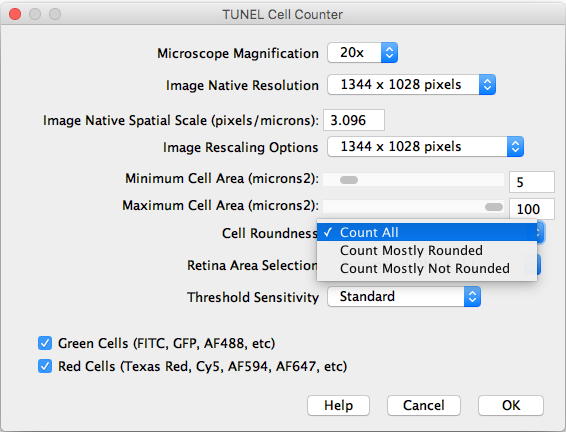
- Cell Roundness: If “All” is selected, all thresholded cells will be counted (Circularity 0-1). If “Mostly rounded“ is selected, mostly circular cells will be counted (Circularity 0.5-1.0). If “Mostly not rounded“ is selected, mostly not circular cells will be counted (Circularity 0.0-0.5).
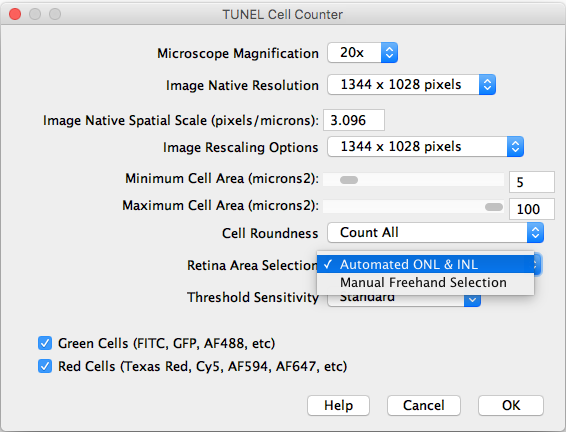
- Retina Area Selection: Choose between automated ONL & INL segmentation or manual freehand selection.
- Threshold Sensitivity: Choose between a standard and high sensitivity threshold, in case you need to detect cells with low intensity values.
- Channels: Choose the cells of interest in either the green, red, or combined channels.
- Help: Links directly to this site.
Results
A processed image is generated and saved in a new directory. Results are saved as an Excel (.xls) file.
Limitations
- Acquisition: The macro was designed for images acquired with a 20x/0.8 air objective. We considered this magnification the most suitable to assess a reasonably large area without missing out cell morphology details.
- Staining quality: Images need to have an intense cell staining and low background noise.
- Image Focus: Uneven image focus will render incomplete layer segmentation.
- Indistinguishable Retinal Layers: The macro cannot distinguish between the ONL and INL if you can't either!
- Uncentered Image: For best results, acquire images centered in frame.
- Significant Shadowing: Shadowing will render incomplete layer segmentation.
To have an idea of suitable images for this macro, we recommend to review the image dataset used for validation:
FAQs
- Q: Can I modify the source code?
- A: Yes, you can modify the code to develop new macros or plugins. Please acknowledge previous work that helped or inspired you, and share your contribution with the scientific community!
- A: Yes, you can modify the code to develop new macros or plugins. Please acknowledge previous work that helped or inspired you, and share your contribution with the scientific community!
- Q: I used this tool for my research. How should I acknowledge it?
- A: Please cite or reference this work as follows: Maidana DE, Tsoka P, Tian B, Dib B, Matsumoto H, Kataoka K, Lin H, Miller JW, Vavvas DG. A Novel ImageJ Macro for Automated Cell Death Quantitation in the Retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:6701–6708. DOI:10.1167/ iovs.15-17599.
- A: Please cite or reference this work as follows: Maidana DE, Tsoka P, Tian B, Dib B, Matsumoto H, Kataoka K, Lin H, Miller JW, Vavvas DG. A Novel ImageJ Macro for Automated Cell Death Quantitation in the Retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:6701–6708. DOI:10.1167/ iovs.15-17599.
- Q: I cannot get accurate segmentation or counting. Any advice?
- A: Check your acquisition and post-processing parameters for the channel of interest. First, reduce background as much as possible to remove any fragments. Next, adjust saturation until cells are easily identifiable. Apply the same settings to the entire dataset if comparison is intended.
- A: Check your acquisition and post-processing parameters for the channel of interest. First, reduce background as much as possible to remove any fragments. Next, adjust saturation until cells are easily identifiable. Apply the same settings to the entire dataset if comparison is intended.
Future Developments
Yes, we know there is a lot to improve!
In case you have any comments, suggestions, or any difficulties with your images, just send us a message!
References
- Maidana DE, Tsoka P, Tian B, Dib B, Matsumoto H, Kataoka K, Lin H, Miller JW, Vavvas DG. A Novel ImageJ Macro for Automated Cell Death Quantitation in the Retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:6701–6708. DOI:10.1167/ iovs.15-17599.
Macro Setup Instructions
How to Download and Install ImageJ Macros
[[Category:]]