Plane Brightness Adjustment Plugin
Authors:
Jan Michalek (michalek at biomed dot cas dot cz)
Martin Capek (capek
at biomed dot cas dot cz)
Jiri Janacek (janacek at
biomed dot cas dot cz)
Source:
Download Plane_Brightness_Adjustment.jar,
change its name to PlaneBrightnessAdjustment.zip and uncompress to retrieve the
source code.
Installation:
Drag and drop Plane_Brightness_Adjustment.jar to
the "ImageJ" window, when "Save
Plugin..." dialog appears, we recommend to put the file in the plugins>Stack
folder. Or download the .jar file to the ImageJ>plugins>Stack folder directly and use Help>Refresh
Menus command. The plugin will then be in the Plugins>Stacks
menu item.
Description:
In images acquired by confocal laser scanning
microscopy (CLSM), regions corresponding to the same concentration of
fluorophores in the specimen should be mapped to the same grayscale
levels. However, in practice, due to multiple distortion effects, CLSM images
of even homogeneous specimen regions suffer from irregular brightness
variations, e.g., darkening of image edges and lightening of the center. The effects are yet more pronounced in images of
real biological specimens. A spatially varying grayscale
map complicates image post-processing, e.g., in alignment of overlapping
regions of two images and in 3D reconstructions, since measures of similarity
usually assume a spatially independent grayscale map.
We present a fast correction method based on estimating a spatially variable
illumination gain, and multiplying acquired CLSM images by the inverse of the
estimated gain. The method does not require any special calibration of
reference images since the gain estimate is extracted from the CLSM image being
corrected itself. The proposed approach exploits two types of morphological
filters: the median filter and the upper Lipschitz
cover.
This plugin is designed to perform processing
on 8-bit grayscale and RGB images, and is able to
work with images in stacks.
Since a median filter of a large kernel is used
in the algorithm, the processing of large images, especially RGB, may be time
consuming.
Dialog box parameters:
Slope means the maximum allowed change (an 8-bit
integer) of the Lipschitz filter between intensities
of two neighboring pixels. Values from 1 to 5 often
yield good results.
Threshold means from which pixel value the adjustment
starts to work. The values below threshold are not corrected.
Maxfactor is a limit imposed on the factor
with which the grayscale values are multiplied to
increase brightness. If too many pixels get saturated by
PlaneBrightnessAdjustment, decrease Maxfactor. If brightness is still inhomogenous
after PlaneBrightnessAdjustment, increase Maxfactor. A value of Maxfactor=8 may
be tried first.
A PDF document and sample confocal stacks (rat embryo fields and rat brain) are available.
References:
See also: Our plugin StackContrastAdjustment.
Example:
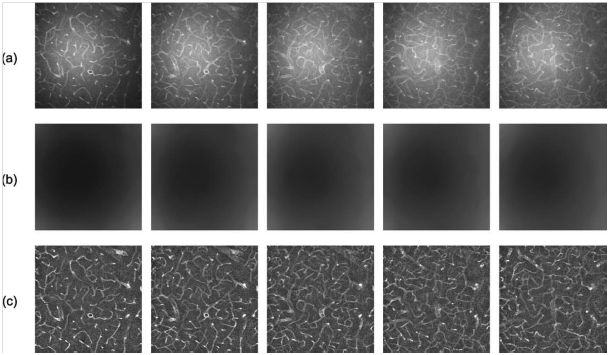
CLSM stack of images 7-microns apart from a rat
brain specimen: (a) the original images, (b) the reciprocal of the Lipschitz-cover estimated gain, (c) images corrected after
applying the upper Lipschitz cover morphological
operator. HC PLAPO 20x water immersion objective (N.A. = 0.70), the excitation
wavelength of 488 nm and emission wavelength range from 500 to 600 nm were
used. The size of each image is 550 x 550 microns.