Thresholded Blur
An edge-preserving averaging (smoothing) algorithm, also known as surface blur.
Description
This ImageJ plugin provides an edge-preserving averaging (smoothing) algorithm. Depending on the parameters and the image type, the filter can even sharpen blurred edges. The filter provides preview and works for all image types (8-, 16-, 32-bit and RGB color).
The algorithm is a selective mean filter with a circular kernel. “Selective” means that pixels strongly deviating from the current pixel are not included in the averaging process.
Limitation: Currently, the filter does not use parallel processing (except for processing of stacks); thus it is rather slow.
Filter parameters
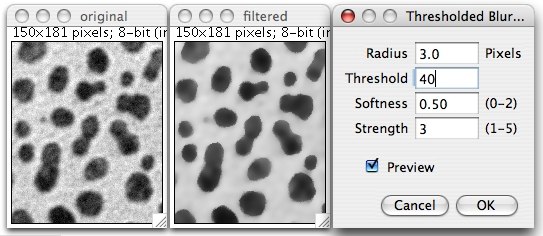
- Radius determines the kernel size included in averaging; see Process>Filters>Show Circular Masks.
- Threshold: Pixels that deviate from the current pixel by more than the threshold are not included in the averaging process. The filter behaves like a usual mean filter if the threshold is larger than the range of the pixels (e.g. 255 for 8-bit images). No filtering is done if threshold = 0. The threshold should be smaller than the pixel difference across edges that should be preserved, but larger than the noise.
- Softness: The threshold can be soft. In this case, if the difference between the neighbor and the pixel is close to the threshold, i.e., within threshold * (1 - softness) and threshold * (1 + softness), it contributes with a weight between 0 and 1. For strength > 1, the equation uses the softness multiplied by the strength value. Typical softness values are between 0 and 2. A soft threshold produces softer edges.
- Strength: For stronger smoothing, use a value of “Strength” > 1. Then, filtering is applied as many times as given by that parameter.
- Brightness-Based: For RGB images, the difference between two pixels can be calculated as the distance between the points (r,g,b) in a cartesian system or as the difference of brightness (brightness-based). In both cases, the weights of the colors can be set in Edit>Options>Conversions.
“Brightness-based” is advisable for images that have stronger color noise than brightness noise.
The filter can be also used to sharpen edges; use strength values > 1 to enhance this effect. On the other hand, if unwanted sharp contours appear in the filtered image (“staircasing” effect), try increasing the softness parameter and use a strength value of 1. Anyhow, thresholded blur (surface blur) is less prone to staircasing than some other edge-preserving blur filters.
Related filters:
- Surface Blur by Douglas Cameron (previously on imagejdocu.tudor.lu, currently not moved to ImageJ.net, available via the wayback machine): Surface blur with a distance-dependent weight of the pixels. For RGB images only.
- Lee’s Sigma Filter: An edge-preserving filter that does not need manual selection of a threshold.
Download
- Source code
Thresholded_Blur.javaon GitHub (make sure you download the raw file, use the button near the top right) - Class file
Thresholded_Blur.classon GitHub
Installation
- Copy the raw
Thresholded_Blur.javafile into the ImageJ plugins folder or a subfolder thereof. Make sure that you name the downloaded file ”Thresholded_Blur.java”; uppercase/lowercase matters. - Compile with “Compile and Run” and press “OK”. Note that “Compile and Run” is currently broken on Fiji; as a workaround use File>New>Script, open the
Thresholded_Blur.javafile and press “Run“. - Alternatively, directly save the .class file
Thresholded_Blur.classinto the ImageJ/plugins directory or an immediate subdirectory thereof. Again, make sure that you name the file correctly, uppercase/lowercase matters. - Use Help>Update Menus or restart ImageJ to make it appear in the Plugins menu (not necessary if you have used the Fiji Script Editor).
Version History
- 2023-08-30 Michael Schmid: Nonblocking dialog, but still not parallelized